Utility-Scale Battery Storage Costs Continue To Drop, EIA Study Finds
23 October 2020
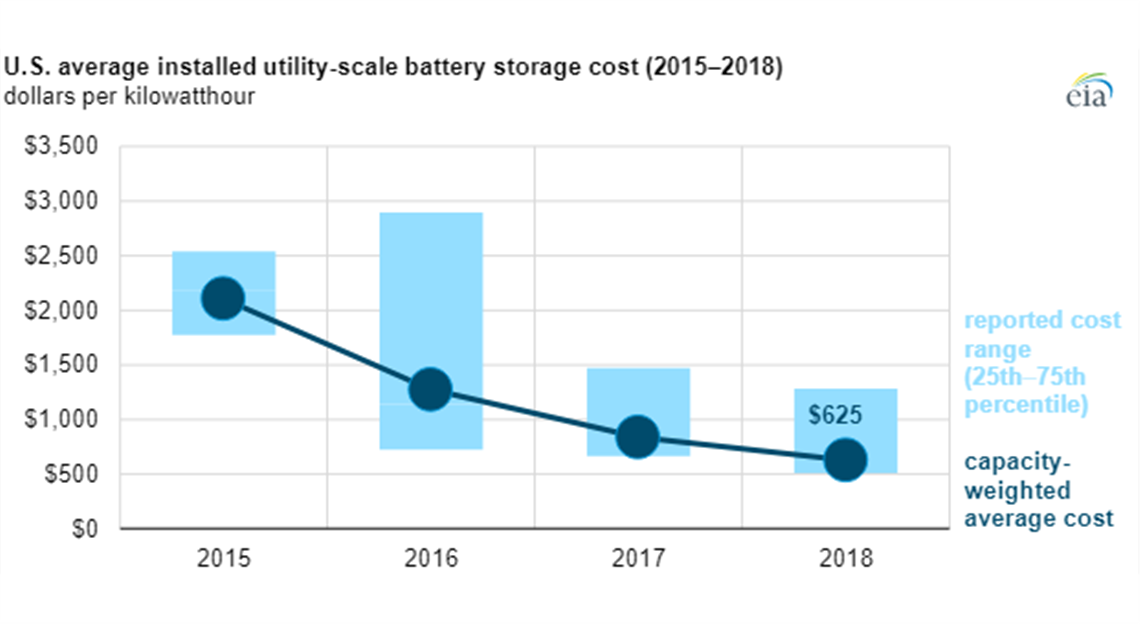
The average energy capacity cost of utility-scale battery storage in the United States has decreased from US$2152 per kWh in 2015 to US$625/kWh in 2018, according to a new report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).
At the end of 2018, the United States had 869 MW of installed battery power capacity (the maximum amount of power a battery can provide at a given moment) and 1236 MWh of battery energy capacity (the total amount of energy that can be stored by a battery), the EIA reports.
Battery storage costs vary by region and application. Independent system operators (ISOs) and regional transmission organizations (RTOs) manage the operation of the U.S. electric system. To understand how battery storage costs vary based on a battery unit’s location, the EIA grouped cost data into regions based on RTOs/ISOs or (such as in the case of California) aggregated different entities in the state to avoid disclosing respondents’ confidential information in areas with fewer battery systems. At the regional level, the 2013 to 2018 average utility-scale battery costs ranged from US$1946/kWh in the PJM Interconnection (PJM), which manages the electric power grid in 13 eastern and midwestern states and the District of Columbia, to as low as US$947/kWh in Hawaii.
Most of the batteries installed in PJM are used for power applications, such as frequency regulation, which helps maintain the grid’s electric frequency on a second-to-second basis. PJM prioritizes power capabilities that use shorter durations over energy use cases that store large amounts of energy over time. For this reason, the power capacity installed cost is a better indicator of price for value in PJM.
California had the most installed battery capacity of any state in 2019. The average battery storage cost in California was US$1522/kWh. About two-thirds of battery storage capacity in California is used for frequency regulation. Batteries in the state also provide energy-oriented services, including ancillary services, black start services, and easing transmission congestion.
According to EIA data, the United States added 152 MW of battery storage capacity in 2019 and added an additional 301 MW in 2020 through July 2020. EIA also collects data on planned future battery capacity additions. Based on planned capacity additions data reported to EIA by developers and power plant owners as of July 2020, EIA expects battery storage to increase by more than 6900 MW in the next few years. About 2300 MW of the 6900 MW of planned battery storage capacity was reported to EIA between April and June 2020. Large battery storage systems are increasingly paired with renewable energy power plants to increase grid reliability and resilience.
POWER SOURCING GUIDE
The trusted reference and buyer’s guide for 83 years
The original “desktop search engine,” guiding nearly 10,000 users in more than 90 countries it is the primary reference for specifications and details on all the components that go into engine systems.
Visit Now
STAY CONNECTED




Receive the information you need when you need it through our world-leading magazines, newsletters and daily briefings.
CONNECT WITH THE TEAM