Read this article in Français Deutsch Italiano Português Español
2025 forecasts show mixed trends: stalls and declines amid growing electrification
22 December 2024
With a new year upon us, the off-highway and commercial vehicle industries face a landscape marked by shifting trends, regional challenges and opportunities for growth. Power Progress asked several industry experts to weigh in on these trends and what we should expect in 2025. Below is a summary of their remarks.
Equipment Markets
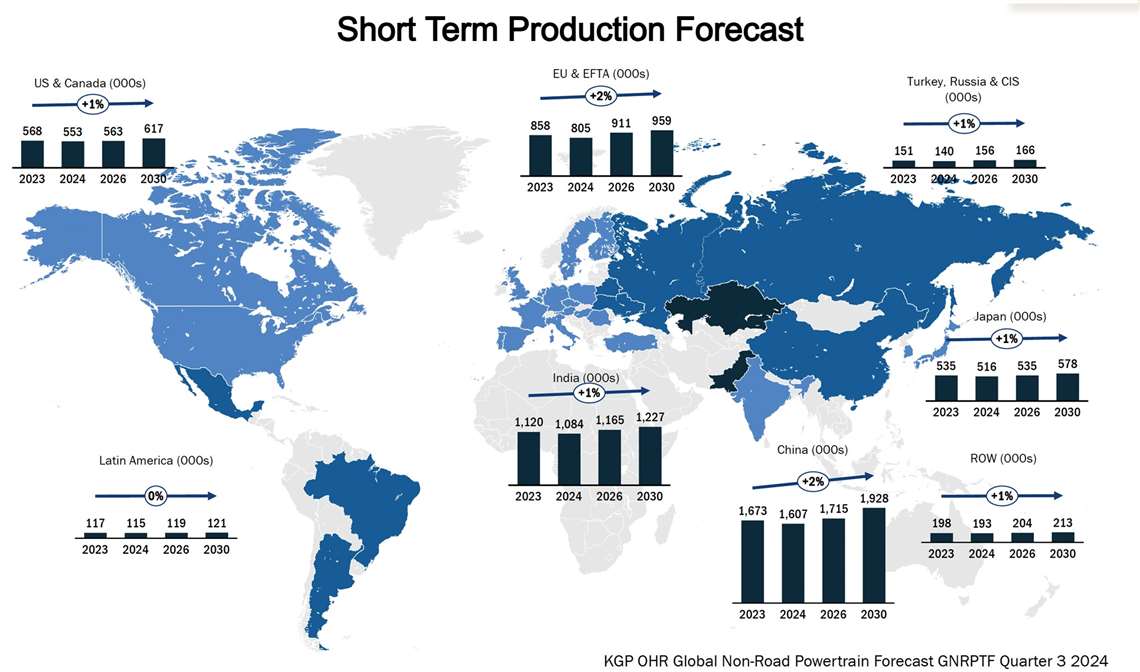
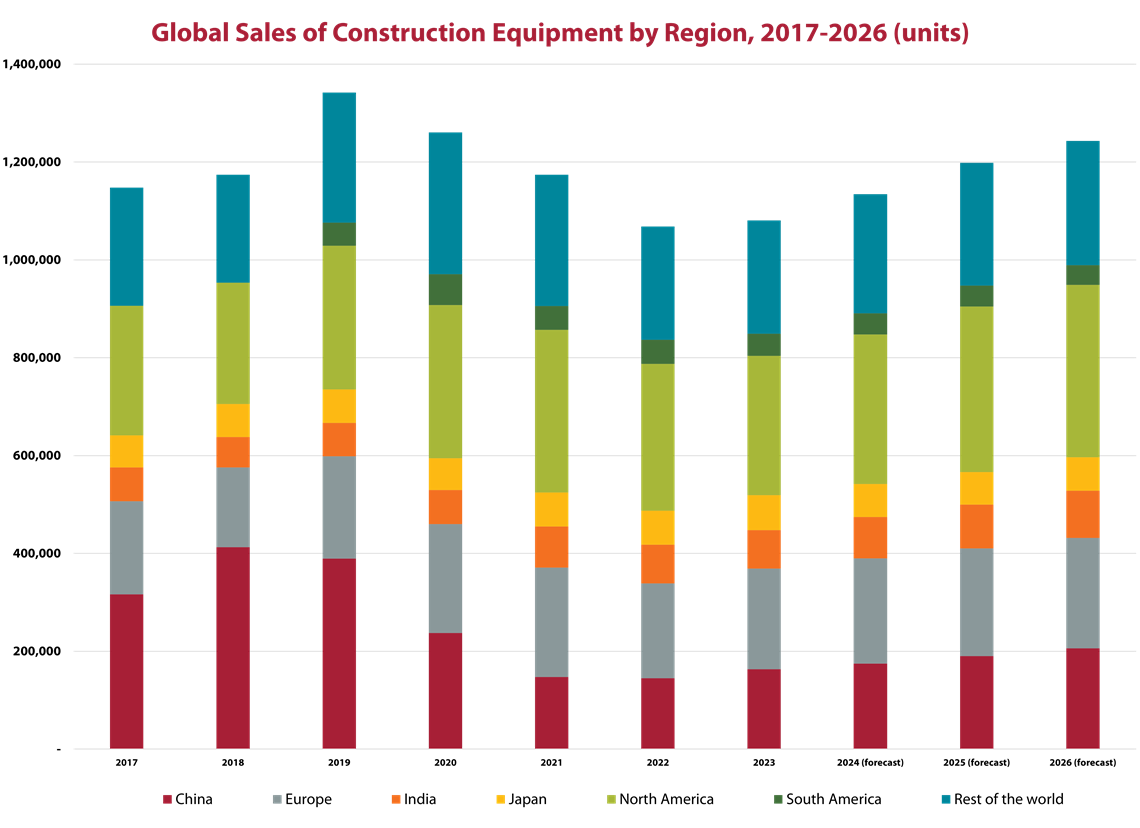
Chris Sleight, managing director of Off-Highway Research, said the global construction equipment market is stabilizing after the unprecedented highs of the pandemic years, which hit a peak globally in 2021 with other markets hitting new highs in the subsequent two years. However, supply chain and logistics bottlenecks during that time also led to a spike in inflation — and higher interest rates intended to temper it.
 Source: Off-Highway Research
Source: Off-Highway Research
While inflation is now under relative control, Sleight said it’s not dropping at a fast enough rate, which has resulted in continued high interest rates. According to Sleight, central bankers raised rates too slowly to curb inflation effectively, “and they are asleep at the wheel again.” Elevated borrowing costs have slowed equipment purchases as well as housing construction, which also affects equipment purchases. Buyers are deferring investments in both until financing becomes more favorable, Sleight said.
As such, he said that 2024 will see declines in the global equipment markets of about 10 percent, which follows declines of 7 percent and 6 percent in 2022 and 2023 respectively.
Despite these challenges, Sleight sees room for optimism. He suggested that pent-up demand may spur a rebound as interest rates decline and aging equipment fleets require replacement. By 2025, the market could enter a growth phase driven by infrastructure investments and more sustainable purchasing trends.
Sleight emphasized that long-term prospects remain strong. He anticipates that not only will interest rates be lower within the next 12 months, but many machines of a late-2010s vintage will need to be replaced.
From a regional perspective, Sleight said that the North American market has cooled in 2024 following three years of record equipment sales. Compact equipment, such as mini excavators and track loaders, remains strong, driven by resilient residential construction, but broader recovery is not expected until late 2025.
In China, he noted that the market continues to struggle with bad debts and weak real estate activity. Some interesting developments, such as scrappage schemes that seek to trade old equipment for newer, more emissions-friendly varieties, are only providing incremental relief.
Meanwhile, Sleight said Europe is grappling with high interest rates and declining housing activity, which have sharply reduced demand for equipment, particularly compact machines. He expects the region to see an equipment sales decline of roughly 14 percent in 2024. Germany’s political instability has not helped, with the recent collapse of the coalition government affecting policymaking in Europe’s largest economy until after late-February elections.
Sales declines are similarly going to result in reduced production. Alex Woodrow, managing director of Knibb, Gormezano and Partners, addressed this by saying production of agricultural, construction and material handling equipment is expected to decline by 4 percent in 2024. Volumes are expected to remain flat in 2025, he said, before climbing again in 2026.
European construction equipment and Japanese ag equipment output are the primary drivers behind the short-term declines, Woodrow said. He echoed Sleight’s analysis of the weakness in the construction equipment market. Regarding ag equipment, high input costs coupled with poor yields are making it difficult for farmers to invest in equipment.
Engine Trends
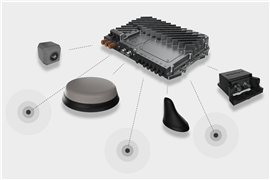
Because it remains clear that internal combustion (IC) engines will continue their central role in powering off-highway equipment, Woodrow also addressed key trends in engines, particularly as the market navigates new emissions regulations and technological advancements.
 Source: Knibb, Gormezano and Partners. KGP OHR Global Non-road Powertrain Forecast, Q3 2024.
Source: Knibb, Gormezano and Partners. KGP OHR Global Non-road Powertrain Forecast, Q3 2024.
In the below-56 kW segment, which is dominated by the agricultural sector, Woodrow said captive supply accounted for 69 percent of production in 2024. This left limited opportunities for non-captive suppliers to expand.
Above 56 kW, by contrast, non-captive supply is more prevalent, Woodrow said, comprising 45 percent of the market. AGCO, for instance, plans to launch innovative engine options such as sub-4.0 L engines to meet evolving demands.
Decarbonization remains a challenge for higher power ranges, and Woodrow noted that hybridization is emerging as the most viable path forward due to the weight, cost and infrastructure constraints of fully battery-electric solutions.
Additionally, new emissions standards, including China State IV and India’s Bharat Stage V, are further shaping the market, spurring pre-buy activity and encouraging advancements in engine efficiency.
While battery-electric power is still limited in high-power applications, gradual improvements in hybrid technologies and infrastructure are helping bridge the gap, particularly in regions with stringent emissions targets.
Electrification Keeps Growing
Nonetheless, electrification continues to affect the off-highway equipment market, with significant growth projected across several segments. Guy Youngs, electrification lead at Power Systems Research (PSR), forecasted a 296 percent increase in electric-powered equipment from 2020 to 2029, with electrified equipment expected to comprise 24.5 percent of the market by the end of that period.
The aforementioned hybridization of equipment is also set to grow rapidly, Youngs said, with a 327 percent increase, though from a much smaller base. These gains are driven by advancements in battery technology, regulatory pressures and cost reductions, he said.
According to Youngs, leading the way in electrification are the lawn and garden and industrial segments.
Lawn and garden equipment, driven by noise and pollution restrictions, is forecasted to grow from 580,000 units in 2020 to 2.6 million units by 2029. Industrial equipment, such as pressure washers, is also seeing rapid electrification, bolstered by cost competitiveness and improved infrastructure.
However, the agriculture and construction segments are lagging. Similar to Woodrow’s remarks, Youngs noted that current electric solutions cannot meet the prolonged duty cycles required in these applications. In the near term, he believes biofuels and methane are more feasible solutions.
Driving growth in electrification are advancements in battery technology, Youngs said, and investments spurred by the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act are driving the development of solid-state batteries and the construction of battery plants in North America. By 2025, nine new facilities with a combined capacity of 257 GWh are expected to come online, he said, with battery costs projected to drop to $80 per kWh by 2026. Youngs highlighted these developments as critical to expanding electrification across all segments.
Policy uncertainty, however, remains a challenge regarding electrification. Youngs and Woodrow both noted that potential federal changes under a Trump administration could reduce incentives for electrification. However, state-level policies, corporate commitments to renewables and global emissions standards are expected to continue their momentum. Youngs noted that electrification adoption rates in the U.S. lag countries like China and the UK, underscoring the need for continued investment and policy support.
Stable Power Generation
Power generation, which supports many markets, from construction to agriculture, will be stable in 2025, according to Romain Mocaer, a consultant with PowerGen Statistics. This stabilization follows the record highs of the pandemic years and a peak in 2023.
Demand is stabilizing following a 5 percent decline in 2024. The outlook for 2025 will be relatively flat, particularly in the low-power segment (<75 kVA). Mocaer said that larger power ranges continue to show resilience, driven by their enduring role in critical applications across construction, heavy industry and telecommunications.
Despite global decarbonization efforts and modest growth in battery energy storage systems (BESS), Mocaer noted the continued dominance of diesel generators in power generation, which remain central to the sub-750 kVA market. In sectors such as rental markets in Europe, batteries are complementing rather than replacing diesel solutions. Mocaer said this highlights the slow adoption of alternative technologies in the power gen industry.
A key development Mocaer noted is the influence of geopolitical and economic uncertainty on regional demand. For instance, Europe faces potential growth opportunities tied to Ukraine’s energy infrastructure rebuild, while economic challenges in South America and much of Africa constrain broader recovery. At the same time, Mocaer said Southeast Asia and India stand out for their robust economic activity and public spending.
On-highway Challenges
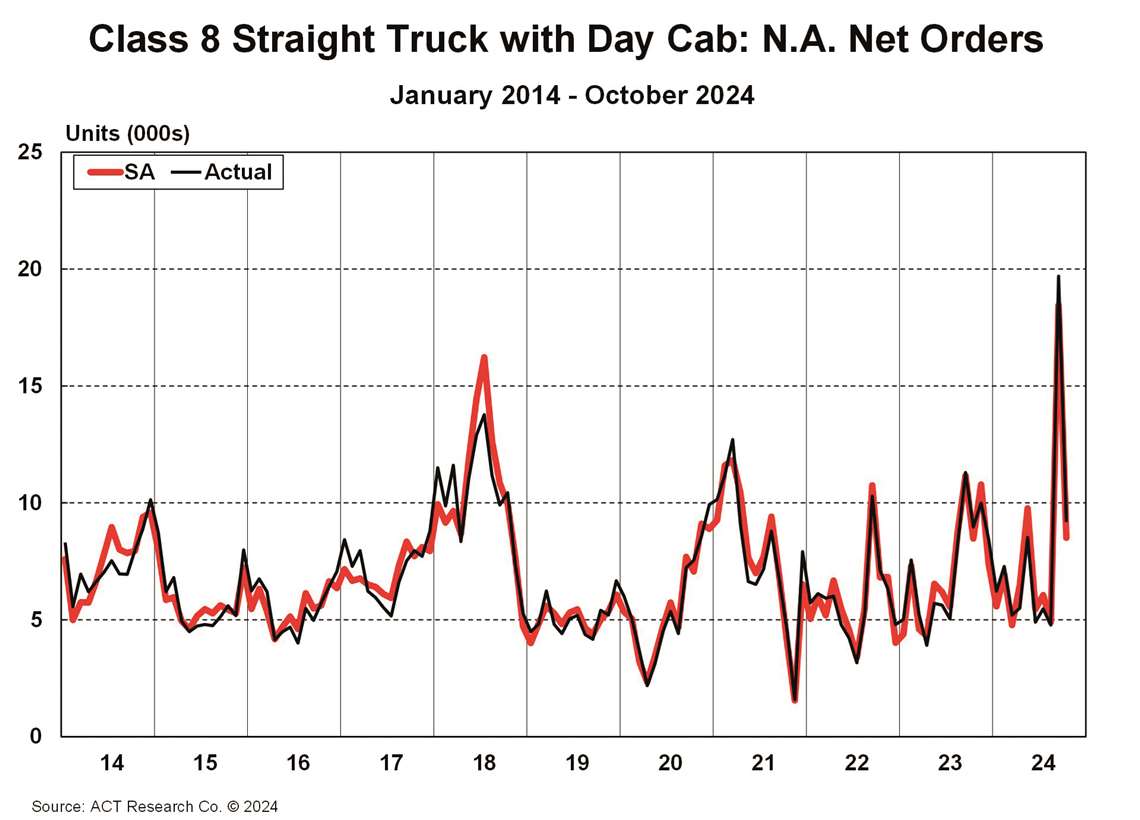
Uncertainty is not only confounding those looking at the off-highway equipment markets. Despite a resilient U.S. economy and easing inflation, Ken Vieth, president and senior analyst at ACT Research, underscored the lack of certainty facing the on-highway market in 2025, driven by both economic pressures and regulatory challenges.
 Source: ACT Research Co.
Source: ACT Research Co.
First, there is regulatory uncertainty, which is a major factor shaping the market outlook. Echoing the concerns related to the Trump administration and the ascendance of the Republican Party in the U.S., Vieth noted that Republicans tend to be more hostile to regulation. That being said, decisions about upcoming regulations will be consequential to the industry, he said.
For example, the EPA’s 2027 Clean Truck and GHG-3 mandates are expected to drive significant pre-buy activity as buyers seek to avoid the costlier, more complex vehicles required by these emissions regulations. However, Vieth said the incoming Trump administration poses risks to this trajectory, with the potential to alter or repeal these mandates. He noted that any changes could reduce pre-buy activity, destabilizing demand and shifting the industry back to organic, market-based levels.
Trade policies under the new administration also add complexity, Vieth said. Potential tariffs and countermeasures could disrupt global supply chains, affecting freight volumes and shifting demand in the commercial vehicle sector. Furthermore, he said labor constraints, exacerbated by potential immigration policies, may further hinder growth in freight and manufacturing.
Despite these challenges, Vieth identified bright spots in the market. Infrastructure investments fueled by the CHIPS Act, the Inflation Reduction Act, and other federal programs are driving demand for vocational trucks, particularly in construction and industrial applications. Vocational markets remain a stronghold, supported by robust manufacturing and infrastructure activity, even as freight markets grapple with overcapacity and subdued profitability.
Editor’s note: as this article reflects several separate forecasts addressing a variety of markets, it was written with the assistance of AI.
POWER SOURCING GUIDE
The trusted reference and buyer’s guide for 83 years
The original “desktop search engine,” guiding nearly 10,000 users in more than 90 countries it is the primary reference for specifications and details on all the components that go into engine systems.
Visit Now
STAY CONNECTED




Receive the information you need when you need it through our world-leading magazines, newsletters and daily briefings.
CONNECT WITH THE TEAM